“Trusted Firmware-A移植”的版本间的差异
(创建页面,内容为“==Trusted Firmware-A简介== ==实验目的== ==实验平台== ==实验步骤== ===导入源码=== ===TF卡分区=== ===建立自己的平台=== ===调整设备树...”) |
(→eMMC移植) |
||
| (未显示同一用户的14个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
==Trusted Firmware-A简介== | ==Trusted Firmware-A简介== | ||
| + | 嵌入式高速发展的今天,大量的嵌入式设备使用了Arm为核心的芯片。我们会接触到越来越多的嵌入式设备,一个问题油然而生:数量如此巨大的嵌入式设备的安全性如何?目前针对嵌入式安全的技术和标准可谓千姿百态,除了必要的硬件安全技术,与之配套的安全软件也是必不可少的一部分。今天我们要介绍的是基于Arm 的可信固件Trusted Firmware-A,简称TF-A。它是一个开源软件,运行在一个硬件隔离的安全环境中并提供安全服务。 | ||
| + | |||
==实验目的== | ==实验目的== | ||
| + | 完成TF-A的基本功能实现TF-A引导u-boot启动。 | ||
| + | |||
==实验平台== | ==实验平台== | ||
| + | 华清远见开发环境,FS-MP1A平台 | ||
| + | |||
==实验步骤== | ==实验步骤== | ||
| + | 本实验基于tf-a-stm32mp-2.2版本,然后添加意法半导体提供的补丁文件。在意法半导体官方的tf-a中移植我们自己的tf-a。 | ||
| + | |||
===导入源码=== | ===导入源码=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 如果之前已经建立了源码目录,并且导入了源码包,即可跳过本小节。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 建立源码目录 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ cd ~ | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ mkdir FS-MP1A | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 将【华清远见-FS-MP1A开发资料\02-程序源码\04-Linux系统移植\01-官方源码】下的en.SOURCES-stm32mp1-openstlinux-5-4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24.tar.xz压缩包,导入到ubuntu下的${HOME}/FS-MP1A目录下。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-1-1.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 解压缩源码包 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ tar xvf en.SOURCES-stm32mp1-openstlinux-5-4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24.tar.xz | ||
| + | |||
| + | 解压完成后得到“stm32mp1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24”目录 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-1-2.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 进入tf-a目录下 | ||
| + | |||
| + | inux@ubuntu:$ cd ~/FS-MP1A/stm32mp1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24/sources/arm-ostl-linux-gnueabi/tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-1-3.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 该目录下以patch结尾的文件为ST官方提供的补丁文件;tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0.tar.gz为标准tf-a源码包。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 解压标准tf-a源码包 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ tar -xvf tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0.tar.gz | ||
| + | |||
| + | 解压完成后得到tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1目录 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-1-4.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 进入tf-a源码目录下: | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ cd tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-1-5.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 将ST官方补丁文件打到tf-a源码中: | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ for p in `ls -1 ../*.patch`; do patch -p1 < $p; done | ||
| + | |||
===TF卡分区=== | ===TF卡分区=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | 要对TF卡进行烧录,需要先将TF接入到ubuntu系统中。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 查看TF卡分区 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ ls /dev/sd* | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-2-1.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 由上图所示只有“/dev/sdb1”一个分区则需要重新进行分区。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 首先删除原有分区 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ sudo parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel msdos | ||
| + | |||
| + | 如果显示如下内容,则表示设备已经被挂载,需要卸载掉设备再删除分区。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-2-2.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 卸载设备 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ umount /dev/sdb1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 卸载完成后重新执行删除分区命令 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ sudo parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel msdos | ||
| + | |||
| + | 对tf进行重新分区 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ sudo sgdisk --resize-table=128 -a 1 -n 1:34:545 -c 1:fsbl1 -n 2:546:1057 -c 2:fsbl2 -n 3:1058:5153 -c 3:ssbl -n 4:5154:136225 -c 4:bootfs -n 5:136226 -c 5:rootfs -A 4:set:2 -p /dev/sdb -g | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-2-3.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color="#FF0000"> | ||
| + | 注意:最后-p /dev/sdb参数中的/dev/sdb需要按照实际ubuntu中的tf节点为准,否则可能发生不可预料的后果。 | ||
| + | </font> | ||
| + | |||
===建立自己的平台=== | ===建立自己的平台=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>配置工具链</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 导入交叉编译工具链(如果还未安装SDK可参考《SDK工具链安装》章节进行安装) | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ source /opt/st/stm32mp1/3.1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24/environment-setup-cortexa7t2hf-neon-vfpv4-ostl-linux-gnueabi | ||
| + | |||
| + | 验证开发工具是否安装正确,显示版本信息如下图所示。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ $CC --version | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:21-2-1.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>增加板级相关文件</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 进入到tf-a源码目录 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ cd ~/FS-MP1A/stm32mp1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24/sources/arm-ostl-linux-gnueabi/tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0/tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 添加设备树文件 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ cp fdts/stm32mp15xx-dkx.dtsi fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ cp fdts/stm32mp157a-dk1.dts fdts/stm32mp157a-fsmp1a.dts | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 修改上层目录下的Makefile.sdk编译脚本在TFA_DEVICETREE配置项中添加stm32mp157a-fsmp1a | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | TFA_DEVICETREE ?= <font color="#FF0000">stm32mp157a-fsmp1a</font> stm32mp157a-dk1 stm32mp157d-dk1 stm32mp157c-dk2 stm32mp157f-dk2 stm32mp157c-ed1 stm32mp157f-ed1 stm32mp157a-ev1 stm32mp157c-ev1 stm32mp157d-ev1 stm32mp157f-ev1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 修改fdts/stm32mp157a-fsmp1a.dts将 | ||
| + | |||
| + | #include "stm32mp15xx-dkx.dtsi" | ||
| + | |||
| + | 修改为 | ||
| + | |||
| + | #include "stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi" | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>编译源码</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 执行如下指令编译trusted: | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ make -f $PWD/../Makefile.sdk TFA_DEVICETREE=stm32mp157a-fsmp1a TF_A_CONFIG=trusted ELF_DEBUG_ENABLE='1' all | ||
| + | |||
| + | 编译成功后,最后显示内容(部分截图)如下: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-3-2.png|1140px]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 编译完成后会在上级build/trusted目录得到如下文件: | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ ls ../ build/trusted | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-3-3.png|1140px]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ cd ../ build/trusted | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>固件烧写</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 由于在移植过程中会多次烧写固件并且会导致正常tf-a无法启动,因此推荐使用TF卡启动的方式来验证。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | tf-a需要使用trusted 格式的u-boot镜像启动,具体的编译方法可参考《U-boot移植》章节中的“生成Trusted镜像”小节。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 将TF接入ubuntu系统后,查看TF卡分区 | ||
| + | |||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ ls /dev/sd* | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-3-4.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | /dev/sdb为TF卡设备。如果该设备下只有/dev/sdb1一个分区则重新分区。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 执行如下指令烧写u-boot: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ sudo dd if=tf-a-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32 of=/dev/sdb1 conv=fdatasync | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ sudo dd if=tf-a-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32 of=/dev/sdb2 conv=fdatasync | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ sudo dd if=u-boot-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32 of=/dev/sdb3 conv=fdatasync | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 其中前两条命令“tf-a-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32”为本章节编译得到的,第三条命令中的“u-boot-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32”则为《U-boot移植》章节中的“生成Trusted镜像”小节得到。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>启动开发板</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 将拨码开关设置为SD卡启动方式: | ||
| + | <table align="center" border="1"> | ||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>Boot mode</td> | ||
| + | <td>BOOT2</td> | ||
| + | <td>BOOT1</td> | ||
| + | <td>BOOT0</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>Engineering boot</td> | ||
| + | <td>1</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>Forced USB bootfor flashing</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>eMMC</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | <td>1</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SDCARD</td> | ||
| + | <td>1</td> | ||
| + | <td>0</td> | ||
| + | <td>1</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 将制作好的TF卡插入开发板,上电后会出现如下错误提示: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-3-5.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 这个错误产生的原因是电源初始化错误,需重新调整电源相关配置 | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
===调整设备树电源配置=== | ===调整设备树电源配置=== | ||
| + | 由于官方参考板DK1采用电源管理芯片做电源管理,而FS-MP1A采用分离电路作为电源管理,本例需要将文件中原有电源管理芯片相关内容去掉,增加上固定电源相关内容 | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>去掉原有电源管理内容</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | DK1参考板电源管理芯片挂在I2C4上,而FS-MP1A并未使用I2C4总线,所以直接将I2C4相关内容完全删除即可。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 修改fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi文件 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 将文件中i2c4节点相关内容整体删除,删除内容如下: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | &i2c4 { | ||
| + | pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep"; | ||
| + | pinctrl-0 = <&i2c4_pins_a>; | ||
| + | pinctrl-1 = <&i2c4_pins_sleep_a>; | ||
| + | i2c-scl-rising-time-ns = <185>; | ||
| + | i2c-scl-falling-time-ns = <20>; | ||
| + | clock-frequency = <400000>; | ||
| + | status = " okay"; | ||
| + | secure-status = "okay"; | ||
| + | /*内容太长此处省略*/ | ||
| + | watchdog { | ||
| + | compatible = "st,stpmic1-wdt"; | ||
| + | status = "disabled"; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | 修改fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi文件,删除如下内容: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | &cpu0{ | ||
| + | cpu-supply = <&vddcore>; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | |||
| + | &cpu1{ | ||
| + | cpu-supply = <&vddcore>; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>添加固定电源配置</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 修改fdts/:文件 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 固定电源配置通常添加在根节点下,在根节点末尾位置添加如下内容(红色字体为需要添加的内容): | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="background-color:#F8F8F8;border:1px solid #E5E5E5;"> | ||
| + | vin: vin {<br> | ||
| + | :: compatible = "regulator-fixed";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-name = "vin";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-min-microvolt = <5000000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-max-microvolt = <5000000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-always-on;<br> | ||
| + | :};<br> | ||
| + | <font color="#FF0000"> | ||
| + | v3v3: regulator-3p3v {<br> | ||
| + | :: compatible = "regulator-fixed";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-name = "v3v3";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-always-on;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-boot-on;<br> | ||
| + | :};<br> | ||
| + | v1v8_audio: regulator-v1v8-audio {<br> | ||
| + | :: compatible = "regulator-fixed";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-name = "v1v8_audio";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-min-microvolt = <1800000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-max-microvolt = <1800000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-always-on;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-boot-on;<br> | ||
| + | :};<br> | ||
| + | v3v3_hdmi: regulator-v3v3-hdmi {<br> | ||
| + | ::compatible = "regulator-fixed";<br> | ||
| + | ::regulator-name = "v3v3_hdmi";<br> | ||
| + | ::regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | ::regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | ::regulator-always-on;<br> | ||
| + | ::regulator-boot-on;<br> | ||
| + | :};<br> | ||
| + | v1v2_hdmi: regulator-v1v2-hdmi {<br> | ||
| + | :: compatible = "regulator-fixed";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-name = "v1v2_hdmi";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-min-microvolt = <1200000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-max-microvolt = <1200000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-always-on;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-boot-on;<br> | ||
| + | :};<br> | ||
| + | vdd: regulator-vdd {<br> | ||
| + | :: compatible = "regulator-fixed";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-name = "vdd";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-always-on;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-boot-on;<br> | ||
| + | :};<br> | ||
| + | vdd_usb: regulator-vdd-usb {<br> | ||
| + | :: compatible = "regulator-fixed";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-name = "vdd_usb";<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-always-on;<br> | ||
| + | :: regulator-boot-on;<br> | ||
| + | :};<br> | ||
| + | </font> | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>重新编译源码</li> | ||
| + | linux@ubuntu:$ make -f $PWD/../Makefile.sdk TFA_DEVICETREE=stm32mp157a-fsmp1a TF_A_CONFIG=trusted ELF_DEBUG_ENABLE='1' all | ||
| + | <li>烧写后启动</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 重新烧写后启动现象如下: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:39-4-4-1.png|1140px]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 可以看到现在已经可以启动到u-boot了 | ||
| + | |||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
===eMMC移植=== | ===eMMC移植=== | ||
| + | 参考原理图可知eMMC使用的是SDMMC2总线,当前所使用的设备树文件中没有SDMMC2的支持,所以需要增加相关内容才能正常驱动eMMC。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center>[[Image:49-1-1-1.png]]</center><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 由于在使STM32MP1芯片很多管脚为多功能复用管脚,且很多管脚具备同样的功能,所以移植eMMC时需要确认硬件设计是使用的是那些管脚,根据原理图确认后管脚对应关系为: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table align="center" border="1"> | ||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>原理图网络编号</td> | ||
| + | <td>对应管脚</td> | ||
| + | <td>管脚功能</td> | ||
| + | <td>管脚功能码</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA0</td> | ||
| + | <td>PB14</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D0</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA1</td> | ||
| + | <td>PB15</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D1</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA2</td> | ||
| + | <td>PB3</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D2</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA3</td> | ||
| + | <td>PB4</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D3</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA4</td> | ||
| + | <td>PA8</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D4</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA5</td> | ||
| + | <td>PA9</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D5</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF10</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA6</td> | ||
| + | <td>PE5</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D6</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_DATA7</td> | ||
| + | <td>PD3</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_D7</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_CLK</td> | ||
| + | <td>PE3</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_CK</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF9</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <tr align="center"> | ||
| + | <td>SD2_CMD</td> | ||
| + | <td>PG6</td> | ||
| + | <td>SDMMC2_CMD</td> | ||
| + | <td>AF10</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li>管脚定义</li> | ||
| + | 在u-boot中STM32MP1默认管脚定义在文件arch/arm/dts/stm32mp15-pinctrl.dtsi中,查看文件中是否有需要的管脚定义: | ||
| + | |||
| + | 查看后确认有SDMMC2的管脚定义,且与FS-MP1A硬件使用情况一致,定义如下: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | sdmmc2_b4_pins_a: sdmmc2-b4-0 { | ||
| + | pins1 { | ||
| + | pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('B', 14, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D0 */ | ||
| + | <STM32_PINMUX('B', 15, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D1 */ | ||
| + | <STM32_PINMUX('B', 3, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D2 */ | ||
| + | <STM32_PINMUX('B', 4, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D3 */ | ||
| + | <STM32_PINMUX('G', 6, AF10)>; /* SDMMC2_CMD */ | ||
| + | slew-rate = <1>; | ||
| + | drive-push-pull; | ||
| + | bias-pull-up; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | pins2 { | ||
| + | pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('E', 3, AF9)>; /* SDMMC2_CK */ | ||
| + | slew-rate = <2>; | ||
| + | drive-push-pull; | ||
| + | bias-pull-up; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | <li>增加SDMMC2节点信息</li> | ||
| + | 修改 fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi增加SDMMC2的信息 | ||
| + | 在原有sdmmc1节点下增加sdmmc2的内容,添加内容可参考arch/arm/dts/stm32mp15xx-edx.dtsi中sdmmc2的写法,内容如下: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | &sdmmc2 { | ||
| + | pinctrl-names = "default"; | ||
| + | pinctrl-0 = <&sdmmc2_b4_pins_a &sdmmc2_d47_pins_a>; | ||
| + | non-removable; | ||
| + | st,neg-edge; | ||
| + | bus-width = <8>; | ||
| + | vmmc-supply = <&v3v3>; | ||
| + | vqmmc-supply = <&v3v3>; | ||
| + | status = "okay"; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | |||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>测试</li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | 重新编译烧写后可以通过ums或者scp的方式更新eMMC中的u-boot即可。具体可参考《通过linux更新eMMC中的u-boot》章节。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | </ol> | ||
2021年3月24日 (三) 13:16的最新版本
目录
Trusted Firmware-A简介
嵌入式高速发展的今天,大量的嵌入式设备使用了Arm为核心的芯片。我们会接触到越来越多的嵌入式设备,一个问题油然而生:数量如此巨大的嵌入式设备的安全性如何?目前针对嵌入式安全的技术和标准可谓千姿百态,除了必要的硬件安全技术,与之配套的安全软件也是必不可少的一部分。今天我们要介绍的是基于Arm 的可信固件Trusted Firmware-A,简称TF-A。它是一个开源软件,运行在一个硬件隔离的安全环境中并提供安全服务。
实验目的
完成TF-A的基本功能实现TF-A引导u-boot启动。
实验平台
华清远见开发环境,FS-MP1A平台
实验步骤
本实验基于tf-a-stm32mp-2.2版本,然后添加意法半导体提供的补丁文件。在意法半导体官方的tf-a中移植我们自己的tf-a。
导入源码
如果之前已经建立了源码目录,并且导入了源码包,即可跳过本小节。
建立源码目录
linux@ubuntu:$ cd ~ linux@ubuntu:$ mkdir FS-MP1A
将【华清远见-FS-MP1A开发资料\02-程序源码\04-Linux系统移植\01-官方源码】下的en.SOURCES-stm32mp1-openstlinux-5-4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24.tar.xz压缩包,导入到ubuntu下的${HOME}/FS-MP1A目录下。
解压缩源码包
linux@ubuntu:$ tar xvf en.SOURCES-stm32mp1-openstlinux-5-4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24.tar.xz
解压完成后得到“stm32mp1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24”目录

进入tf-a目录下
inux@ubuntu:$ cd ~/FS-MP1A/stm32mp1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24/sources/arm-ostl-linux-gnueabi/tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0

该目录下以patch结尾的文件为ST官方提供的补丁文件;tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0.tar.gz为标准tf-a源码包。
解压标准tf-a源码包
linux@ubuntu:$ tar -xvf tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0.tar.gz
解压完成后得到tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1目录

进入tf-a源码目录下:
linux@ubuntu:$ cd tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1

将ST官方补丁文件打到tf-a源码中:
linux@ubuntu:$ for p in `ls -1 ../*.patch`; do patch -p1 < $p; done
TF卡分区
要对TF卡进行烧录,需要先将TF接入到ubuntu系统中。
查看TF卡分区
linux@ubuntu:$ ls /dev/sd*
由上图所示只有“/dev/sdb1”一个分区则需要重新进行分区。
首先删除原有分区
linux@ubuntu:$ sudo parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel msdos
如果显示如下内容,则表示设备已经被挂载,需要卸载掉设备再删除分区。
卸载设备
linux@ubuntu:$ umount /dev/sdb1
卸载完成后重新执行删除分区命令
linux@ubuntu:$ sudo parted -s /dev/sdb mklabel msdos
对tf进行重新分区
linux@ubuntu:$ sudo sgdisk --resize-table=128 -a 1 -n 1:34:545 -c 1:fsbl1 -n 2:546:1057 -c 2:fsbl2 -n 3:1058:5153 -c 3:ssbl -n 4:5154:136225 -c 4:bootfs -n 5:136226 -c 5:rootfs -A 4:set:2 -p /dev/sdb -g
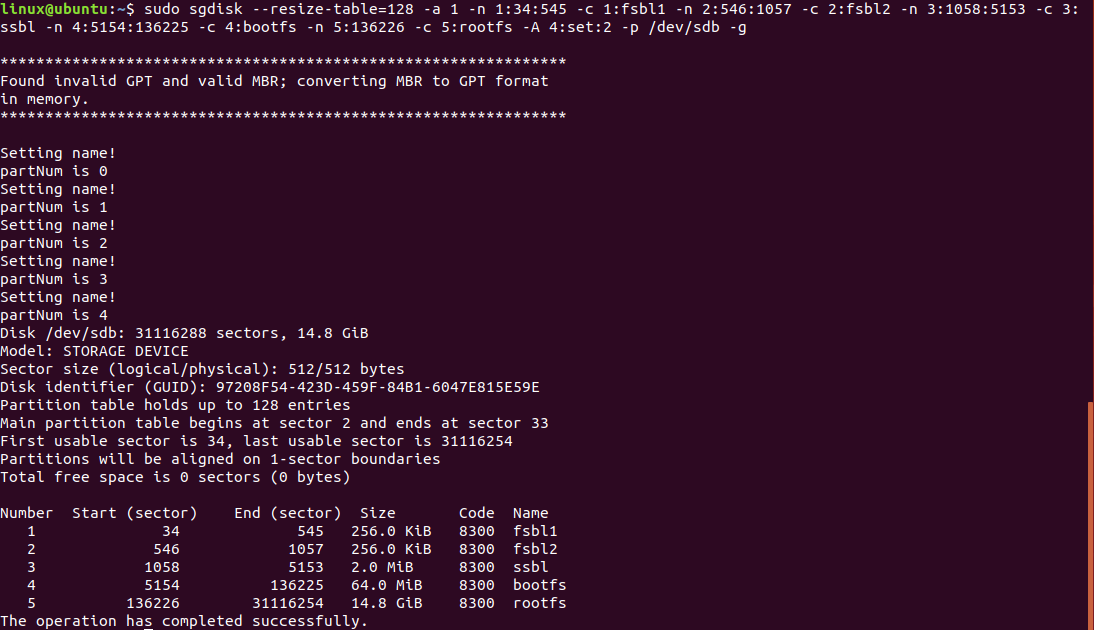
注意:最后-p /dev/sdb参数中的/dev/sdb需要按照实际ubuntu中的tf节点为准,否则可能发生不可预料的后果。
建立自己的平台
- 配置工具链
- 增加板级相关文件
- 编译源码
- 固件烧写
- 启动开发板
导入交叉编译工具链(如果还未安装SDK可参考《SDK工具链安装》章节进行安装)
linux@ubuntu:$ source /opt/st/stm32mp1/3.1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24/environment-setup-cortexa7t2hf-neon-vfpv4-ostl-linux-gnueabi
验证开发工具是否安装正确,显示版本信息如下图所示。
linux@ubuntu:$ $CC --version

进入到tf-a源码目录
linux@ubuntu:$ cd ~/FS-MP1A/stm32mp1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24/sources/arm-ostl-linux-gnueabi/tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1-r0/tf-a-stm32mp-2.2.r1
添加设备树文件
linux@ubuntu:$ cp fdts/stm32mp15xx-dkx.dtsi fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi linux@ubuntu:$ cp fdts/stm32mp157a-dk1.dts fdts/stm32mp157a-fsmp1a.dts
修改上层目录下的Makefile.sdk编译脚本在TFA_DEVICETREE配置项中添加stm32mp157a-fsmp1a
TFA_DEVICETREE ?= stm32mp157a-fsmp1a stm32mp157a-dk1 stm32mp157d-dk1 stm32mp157c-dk2 stm32mp157f-dk2 stm32mp157c-ed1 stm32mp157f-ed1 stm32mp157a-ev1 stm32mp157c-ev1 stm32mp157d-ev1 stm32mp157f-ev1
修改fdts/stm32mp157a-fsmp1a.dts将
#include "stm32mp15xx-dkx.dtsi"
修改为
#include "stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi"
执行如下指令编译trusted:
linux@ubuntu:$ make -f $PWD/../Makefile.sdk TFA_DEVICETREE=stm32mp157a-fsmp1a TF_A_CONFIG=trusted ELF_DEBUG_ENABLE='1' all
编译成功后,最后显示内容(部分截图)如下:
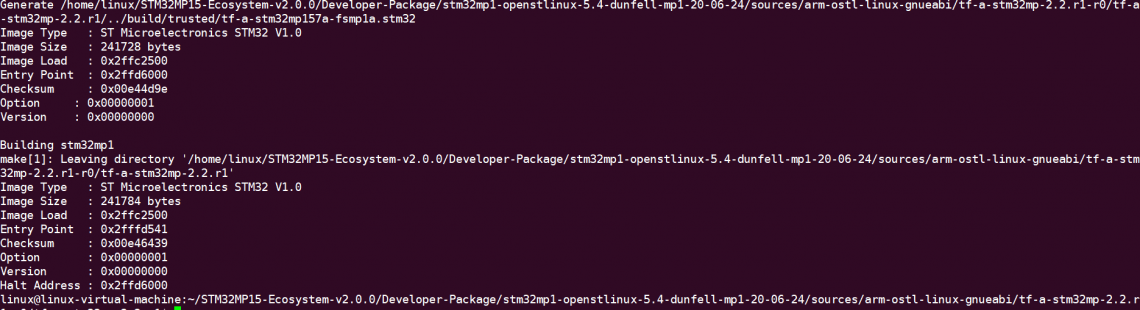
编译完成后会在上级build/trusted目录得到如下文件:
linux@ubuntu:$ ls ../ build/trusted
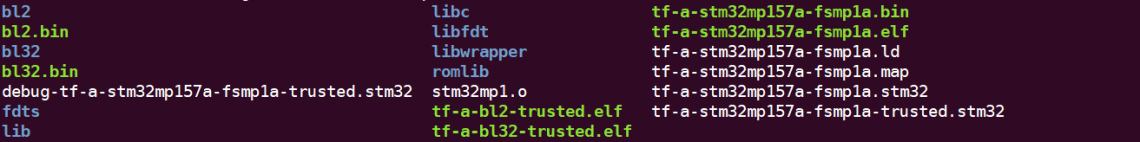
linux@ubuntu:$ cd ../ build/trusted
由于在移植过程中会多次烧写固件并且会导致正常tf-a无法启动,因此推荐使用TF卡启动的方式来验证。
tf-a需要使用trusted 格式的u-boot镜像启动,具体的编译方法可参考《U-boot移植》章节中的“生成Trusted镜像”小节。
将TF接入ubuntu系统后,查看TF卡分区
linux@ubuntu:$ ls /dev/sd*

/dev/sdb为TF卡设备。如果该设备下只有/dev/sdb1一个分区则重新分区。
执行如下指令烧写u-boot:
linux@ubuntu:$ sudo dd if=tf-a-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32 of=/dev/sdb1 conv=fdatasync linux@ubuntu:$ sudo dd if=tf-a-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32 of=/dev/sdb2 conv=fdatasync linux@ubuntu:$ sudo dd if=u-boot-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32 of=/dev/sdb3 conv=fdatasync
其中前两条命令“tf-a-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32”为本章节编译得到的,第三条命令中的“u-boot-stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-trusted.stm32”则为《U-boot移植》章节中的“生成Trusted镜像”小节得到。
将拨码开关设置为SD卡启动方式:
| Boot mode | BOOT2 | BOOT1 | BOOT0 |
| Engineering boot | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Forced USB bootfor flashing | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| eMMC | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| SDCARD | 1 | 0 | 1 |
将制作好的TF卡插入开发板,上电后会出现如下错误提示:

这个错误产生的原因是电源初始化错误,需重新调整电源相关配置
调整设备树电源配置
由于官方参考板DK1采用电源管理芯片做电源管理,而FS-MP1A采用分离电路作为电源管理,本例需要将文件中原有电源管理芯片相关内容去掉,增加上固定电源相关内容
- 去掉原有电源管理内容
- 添加固定电源配置
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- regulator-name = "vin";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <5000000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <5000000>;
- regulator-always-on;
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- };
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- regulator-name = "v3v3";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-always-on;
- regulator-boot-on;
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- };
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- regulator-name = "v1v8_audio";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1800000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <1800000>;
- regulator-always-on;
- regulator-boot-on;
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- };
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- regulator-name = "v3v3_hdmi";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-always-on;
- regulator-boot-on;
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- };
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- regulator-name = "v1v2_hdmi";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <1200000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <1200000>;
- regulator-always-on;
- regulator-boot-on;
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- };
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- regulator-name = "vdd";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-always-on;
- regulator-boot-on;
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- };
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- regulator-name = "vdd_usb";
- regulator-min-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-max-microvolt = <3300000>;
- regulator-always-on;
- regulator-boot-on;
- compatible = "regulator-fixed";
- };
- 重新编译源码
- 烧写后启动
DK1参考板电源管理芯片挂在I2C4上,而FS-MP1A并未使用I2C4总线,所以直接将I2C4相关内容完全删除即可。
修改fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi文件
将文件中i2c4节点相关内容整体删除,删除内容如下:
&i2c4 {
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
pinctrl-0 = <&i2c4_pins_a>;
pinctrl-1 = <&i2c4_pins_sleep_a>;
i2c-scl-rising-time-ns = <185>;
i2c-scl-falling-time-ns = <20>;
clock-frequency = <400000>;
status = " okay";
secure-status = "okay";
/*内容太长此处省略*/
watchdog {
compatible = "st,stpmic1-wdt";
status = "disabled";
};
};
};
修改fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi文件,删除如下内容:
&cpu0{
cpu-supply = <&vddcore>;
};
&cpu1{
cpu-supply = <&vddcore>;
};
修改fdts/:文件
固定电源配置通常添加在根节点下,在根节点末尾位置添加如下内容(红色字体为需要添加的内容):
vin: vin {
v3v3: regulator-3p3v {
v1v8_audio: regulator-v1v8-audio {
v3v3_hdmi: regulator-v3v3-hdmi {
v1v2_hdmi: regulator-v1v2-hdmi {
vdd: regulator-vdd {
vdd_usb: regulator-vdd-usb {
};
linux@ubuntu:$ make -f $PWD/../Makefile.sdk TFA_DEVICETREE=stm32mp157a-fsmp1a TF_A_CONFIG=trusted ELF_DEBUG_ENABLE='1' all
重新烧写后启动现象如下:
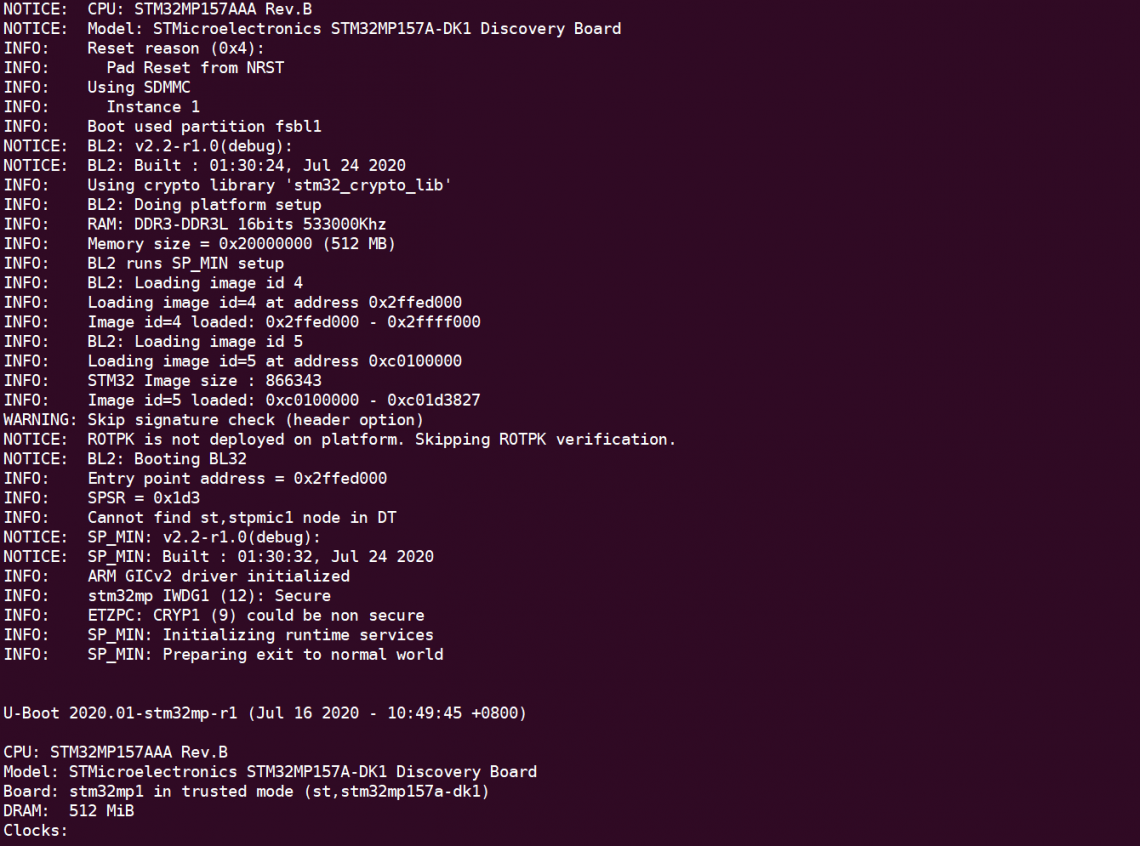
可以看到现在已经可以启动到u-boot了
eMMC移植
参考原理图可知eMMC使用的是SDMMC2总线,当前所使用的设备树文件中没有SDMMC2的支持,所以需要增加相关内容才能正常驱动eMMC。
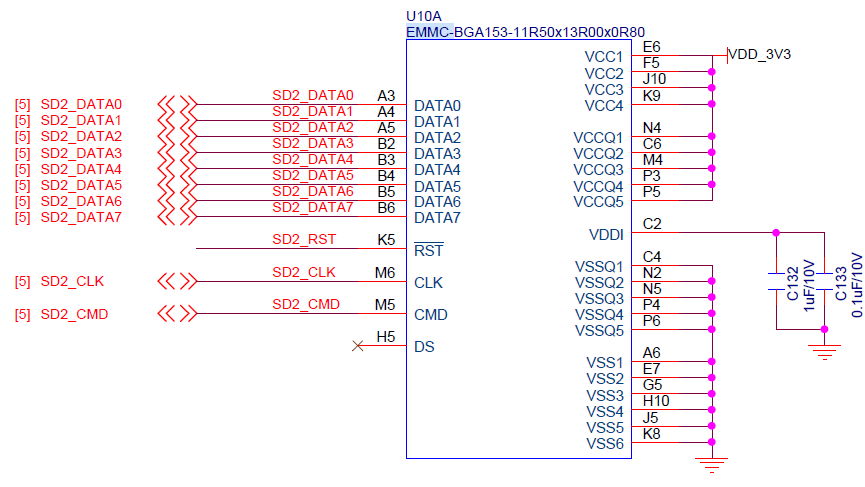
由于在使STM32MP1芯片很多管脚为多功能复用管脚,且很多管脚具备同样的功能,所以移植eMMC时需要确认硬件设计是使用的是那些管脚,根据原理图确认后管脚对应关系为:
| 原理图网络编号 | 对应管脚 | 管脚功能 | 管脚功能码 |
| SD2_DATA0 | PB14 | SDMMC2_D0 | AF9 |
| SD2_DATA1 | PB15 | SDMMC2_D1 | AF9 |
| SD2_DATA2 | PB3 | SDMMC2_D2 | AF9 |
| SD2_DATA3 | PB4 | SDMMC2_D3 | AF9 |
| SD2_DATA4 | PA8 | SDMMC2_D4 | AF9 |
| SD2_DATA5 | PA9 | SDMMC2_D5 | AF10 |
| SD2_DATA6 | PE5 | SDMMC2_D6 | AF9 |
| SD2_DATA7 | PD3 | SDMMC2_D7 | AF9 |
| SD2_CLK | PE3 | SDMMC2_CK | AF9 |
| SD2_CMD | PG6 | SDMMC2_CMD | AF10 |
- 管脚定义
- 增加SDMMC2节点信息
- 测试
在u-boot中STM32MP1默认管脚定义在文件arch/arm/dts/stm32mp15-pinctrl.dtsi中,查看文件中是否有需要的管脚定义:
查看后确认有SDMMC2的管脚定义,且与FS-MP1A硬件使用情况一致,定义如下:
sdmmc2_b4_pins_a: sdmmc2-b4-0 {
pins1 {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('B', 14, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D0 */
<STM32_PINMUX('B', 15, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D1 */
<STM32_PINMUX('B', 3, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D2 */
<STM32_PINMUX('B', 4, AF9)>, /* SDMMC2_D3 */
<STM32_PINMUX('G', 6, AF10)>; /* SDMMC2_CMD */
slew-rate = <1>;
drive-push-pull;
bias-pull-up;
};
pins2 {
pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('E', 3, AF9)>; /* SDMMC2_CK */
slew-rate = <2>;
drive-push-pull;
bias-pull-up;
};
};
修改 fdts/stm32mp15xx-fsmp1x.dtsi增加SDMMC2的信息 在原有sdmmc1节点下增加sdmmc2的内容,添加内容可参考arch/arm/dts/stm32mp15xx-edx.dtsi中sdmmc2的写法,内容如下:
&sdmmc2 {
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&sdmmc2_b4_pins_a &sdmmc2_d47_pins_a>;
non-removable;
st,neg-edge;
bus-width = <8>;
vmmc-supply = <&v3v3>;
vqmmc-supply = <&v3v3>;
status = "okay";
};
重新编译烧写后可以通过ums或者scp的方式更新eMMC中的u-boot即可。具体可参考《通过linux更新eMMC中的u-boot》章节。