扩展板振动马达驱动移植
实验原理
打开扩展板原理图对照扩展板可以看到扩展板有1个振动马达M1,如下图:
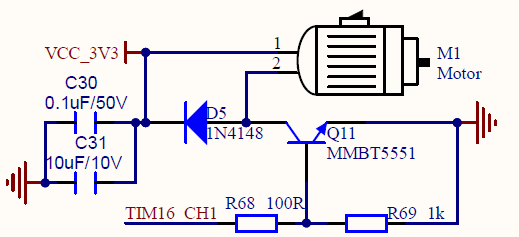
由上图可见可通过TIM16_CH1电平改变控制电路的通断从而驱动线性马达。
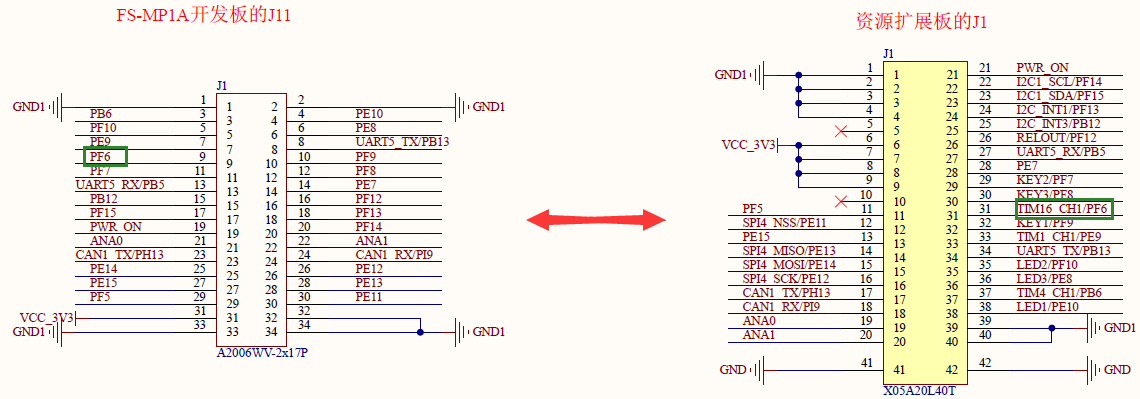
查看原理图可知TIM16_CH1对应PF6,查看芯片手册可知PF6可以作为PWM TIMER16的通道1使用,本文实现如何通过PWM驱动振动马达:
| 原理图网络编号 | 对应管脚 | 管脚功能 | 管脚功能码 |
|---|---|---|---|
| TIM16_CH1 | PF6 | TIM16_CH1 | AF1 |
实验平台
华清远见开发环境,FS-MP1A平台
实验步骤
- 导入交叉编译工具链
- 内核配置
- 修改设备树
- ……
- pwm16_pins_a: pwm16-0 {
- pins {
- pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('F', 6, AF1)>; /* TIM16_CH1 */
- bias-pull-down;
- drive-push-pull;
- slew-rate = <0>;
- };
- pins {
- };
- pwm16_sleep_pins_a: pwm16-sleep-0 {
- pins {
- pinmux = <STM32_PINMUX('F', 6, ANALOG)>; /* TIM16_CH1 */
- };
- pins {
- };
- 重新编译内核和设备树文件
- 更新系统内核和设备树
- 测试
linux@ubuntu:$ source /opt/st/stm32mp1/3.1-openstlinux-5.4-dunfell-mp1-20-06-24/environment-setup-cortexa7t2hf-neon-vfpv4-ostl-linux-gnueabi
内核中为振动马达提供了标准的驱动,只要在内核中配置对应选项即可,驱动路径为:
drivers/input/misc/pwm- vibra.c
执行make menuconfig配置内核对应选项
linux@ubuntu:$ make menuconfig Device Drivers ---> Input device support ---> [*] Miscellaneous devices ---> <*> PWM vibrator support
参考linux内核文档:
Documentation/devicetree/bindings/pwm/pwm-stm32.txt Documentation/devicetree/bindings/input/pwm-vibrator.txt
修改设备树文件:
arch/arm/boot/dts/stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-extended.dts
由于timers16在stm32mp151.dtsi中已完成定义,这里需要在原有基础添加与硬件对应的相关信息,在文件stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-extended.dts末尾继承并添加timers16相关内容:
&timers16 {
/* spare dmas for other usage */
/delete-property/dmas;
/delete-property/dma-names;
status = "okay";
pwm16: pwm {
pinctrl-0 = <&pwm16_pins_a>;
pinctrl-1 = <&pwm16_sleep_pins_a>;
pinctrl-names = "default", "sleep";
#pwm-cells = <2>;
status = "okay";
};
timer@16 {
status = "disabled";
};
};
仿照设备树对于pwm管脚的配置添加timers16 pwm输出管脚配置,在stm32mp157a-fsmp1a-extended.dts文件pinctrl节点中添加pwm16管脚信息,红色字体内容为添加内容:
&pinctrl {
};
最后在根节点下添加振动马达驱动对应节点:
vibrator {
compatible = "pwm-vibrator";
pwms = <&pwm16 0 4000000>;
pwm-names = "enable";
direction-duty-cycle-ns = <10000000>;
};
linux@ubuntu:$ make -j4 uImage dtbs LOADADDR=0xC2000040
系统启动后可以查看目录/dev/input
root@fsmp1a:~# ls /dev/input/ by-path event0 event1 event2
如果系统中有多个input设备,这里可能会有很对eventx,确定哪个event文件是我们的设备文件,可以通过查看/dev/input/by-path或查看dmesg系统启动信息确认:
查看by-path目录下文件
root@fsmp1a:~# ls /dev/input/by-path/ -l total 0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 May 30 08:43 platform-40013000.i2c-event -> ../event2 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jun 30 07:40 platform-beeper-event -> ../event0 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jun 30 07:40 platform-vibrator-event -> ../event1
由显示信息可以确认event1是振动马达的设备文件
编写测试程序测试:
编写测试程序或参考:“光盘资料:华清远见-FS-MP1A开发资料\02-程序源码\06-资源扩展板测试程序\02-vibrator_test”
pwm-vibrator.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
int main(const int argc, const char **argv)
{
int fd;
if (argc != 2) {
printf("usage: %s <device-file>\n", argv[0]);
return 1;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("Error opening file '%s': %s\n", argv[1], strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
int num_effects;
if (ioctl(fd, EVIOCGEFFECTS, &num_effects) < 0) {
printf("Error getting number of effects playable at the same time: %s\n",
strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
printf("%d effects playable at the same time\n", num_effects);
struct ff_effect effect;
effect.type = FF_RUMBLE,
effect.id = -1,
effect.u.rumble.strong_magnitude = 0xFFFF; //调节振动强度
effect.u.rumble.weak_magnitude = 0;
effect.replay.length = 3000; //调节振动时长ms
effect.replay.delay = 0;
if (ioctl(fd, EVIOCSFF, &effect) < 0) {
printf("Error creating new effect: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
printf("New effect ID: %d\n", effect.id);
struct input_event play = {
.type = EV_FF,
.code = effect.id,
.value = 1
};
if (write(fd, (const void*) &play, sizeof(play)) < 0) {
printf("Error writing effect to file: %s\n", strerror(errno));
return 1;
}
printf("Wrote effect\n");
sleep(3);
return 0;
}
交叉编译测试程序并将编译好的测试程序下载到板子上,执行程序如下:
root@fsmp1a:~# ./vibrator_test /dev/input/event1 16 effects playable at the same time New effect ID: 0 Wrote effect
这时可以听到振动马达振动的声音。